Effluent Treatment Plants: Managing Industrial Waste Responsibly
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) play a pivotal role in maintaining environmental sustainability by treating industrial wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. They are crucial for industries across various sectors, including manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, textiles, and food processing, among others. ETPs are designed to remove harmful pollutants, chemicals, and contaminants from wastewater, ensuring that the discharged water meets regulatory
standards and poses minimal risk to ecosystems and public health.
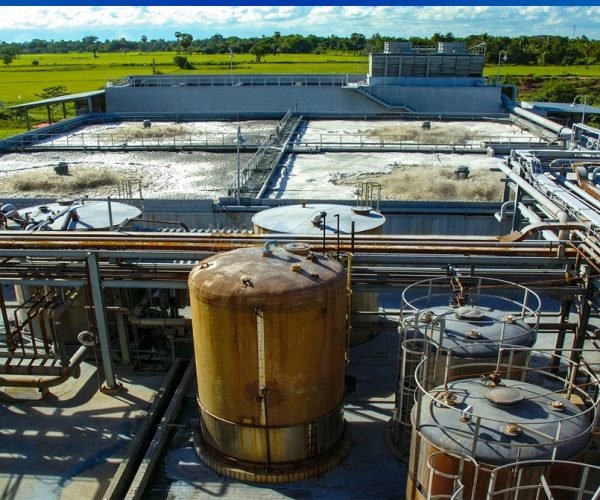

Components and Processes:
ETPs typically consist of several key components and utilize various treatment
processes to effectively treat wastewater. Some common components and
processes include:
Screening and Pre-treatment:
Wastewater undergoes initial screening to
remove large objects, such as debris, plastics, and solids. Pre-treatment processes like sedimentation and equalization help in the removal of settleable solids and the equalization of flow rates and pollutant
concentrations.
Physical Treatment:
Physical treatment methods such as coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration are employed to remove suspended solids, colloidal particles, and other physical impurities from the wastewater.
Chemical Treatment:
Chemical treatment involves the addition of specific chemicals to the wastewater to facilitate the removal of dissolved pollutants, heavy metals, and organic compounds through processes like precipitation, oxidation, and chemical coagulation.
Biological Treatment:
Biological treatment utilizes microorganisms to biodegrade organic pollutants present in the wastewater. Processes like activated sludge treatment, aerobic and anaerobic digestion, and biofiltration are commonly used to break down organic matter into simpler, less harmful substances.
Disinfection:
Disinfection is the final step in the treatment process, aimed at eliminating pathogenic microorganisms and bacteria present in the treated wastewater. Common disinfection methods include chlorination, ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, and ozonation.
Significance and Benefits
The implementation of ETPs offers several significant benefits to both industries and the environment:

Compliance with Regulations
ETPs help industries comply with stringent
environmental regulations and standards governing the discharge of wastewater. By treating wastewater to meet regulatory requirements, industries avoid fines, penalties, and legal consequences associated with non-compliance.
Protection of Ecosystems
Effective treatment of industrial wastewater
minimizes its adverse impact on aquatic ecosystems, soil quality, and groundwater resources. By removing harmful pollutants and contaminants, ETPs safeguard the biodiversity and ecological balance of surrounding habitats.

Resource Conservation
ETPs promote the conservation of water resources by treating and recycling wastewater for non-potable uses within industrial facilities. This reduces the demand for freshwater sources and alleviates the strain on water supplies, particularly in regions facing water scarcity.

Public Health Protection
Proper treatment of wastewater through ETPs helps prevent the contamination of drinking water sources and reduces the risk of waterborne diseases and health hazards associated with exposure to polluted water.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Investing in ETPs demonstrates a company 's commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainable practices, enhancing its reputation and credibility among stakeholders, customers, and the community.
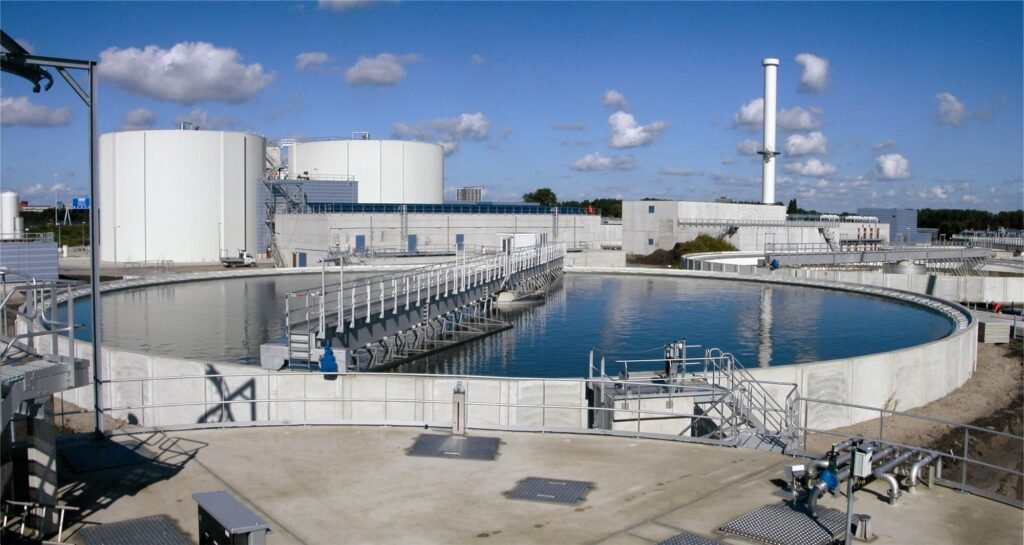

Challenges and Future Outlook:
Despite their numerous benefits, ETPs also face several challenges, including technological complexity, operational costs, maintenance requirements, and the need for continuous monitoring and compliance. Moreover, emerging contaminants, such as pharmaceutical residues, microplastics, and industrial chemicals, pose new challenges for wastewater treatment.
In the future, advancements in ETP technologies, such as the adoption of membrane filtration, advanced oxidation processes, and artificial intelligence for process optimization and control, hold promise for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of wastewater treatment. Additionally, greater emphasis on decentralized treatment systems, water reuse, and circular economy principles can further enhance the sustainability of industrial wastewater management practices.
Conclusion
Effluent Treatment Plants(ETPs)
Effluent Treatment Plants play a vital role in mitigating the environmental impact of industrial activities by treating wastewater and ensuring its safe disposal or reuse. As industries continue to grow and environmental concerns intensify, the implementation of robust ETPs becomes increasingly imperative for achieving sustainable development goals and safeguarding the health of ecosystems and communities worldwide. Through ongoing innovation, collaboration, and regulatory enforcement, ETPs will continue to evolve as indispensable assets in the quest for a cleaner, healthier planet.
