Extended Aeration Sewage Treatment Plant
An Extended Aeration Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) is a biological treatment system designed to efficiently and economically treat wastewater. This approach extends the contact
time between microorganisms and sewage, allowing for thorough biological treatment.
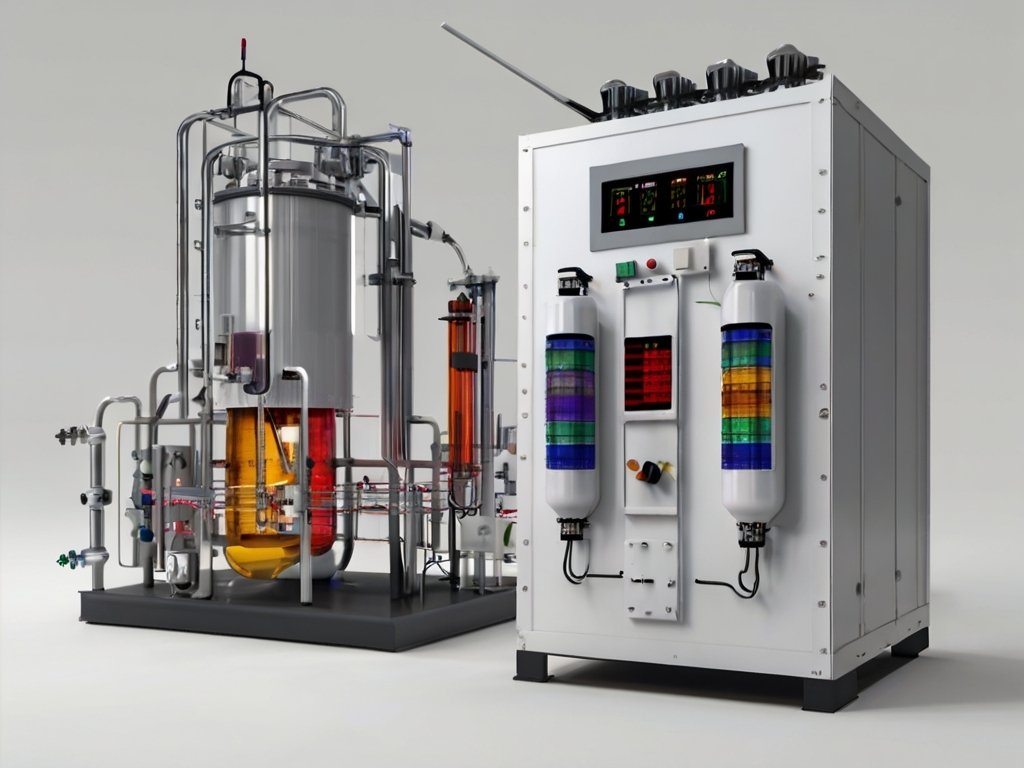

Key Components and Operation:
Aeration Tank:
The heart of the extended aeration system is the aeration tank, where wastewater is introduced, and aeration provides oxygen for the growth of aerobic microorganisms.
Extended Aeration Process:
In extended aeration, the treatment process involves keeping the wastewater in the aeration tank for an extended period, typically 18 to 20 hours. This prolonged contact time allows microorganisms to effectively break down organic pollutants.
Aeration System:
The aeration system supplies oxygen to support the aerobic microbial activity.
Diffused air or mechanical aerators ensure proper mixing and oxygen transfer
throughout the aeration tank.
Sludge Recirculation:
Some extended aeration systems incorporate sludge recirculation to maintain a healthy microbial population. Returning a portion of the settled sludge to the aeration tank promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
Clarification Tank:
After the extended aeration process, the treated water and activated sludge move to a secondary clarifier. In this tank, sludge settles, and the clarified effluent is separated from the biomass.
Disinfection (Optional):
Depending on regulatory requirements, the effluent may undergo disinfection
(e.g., chlorination or UV treatment) before discharge to ensure the removal of remaining pathogens.
Schematic Block Diagram
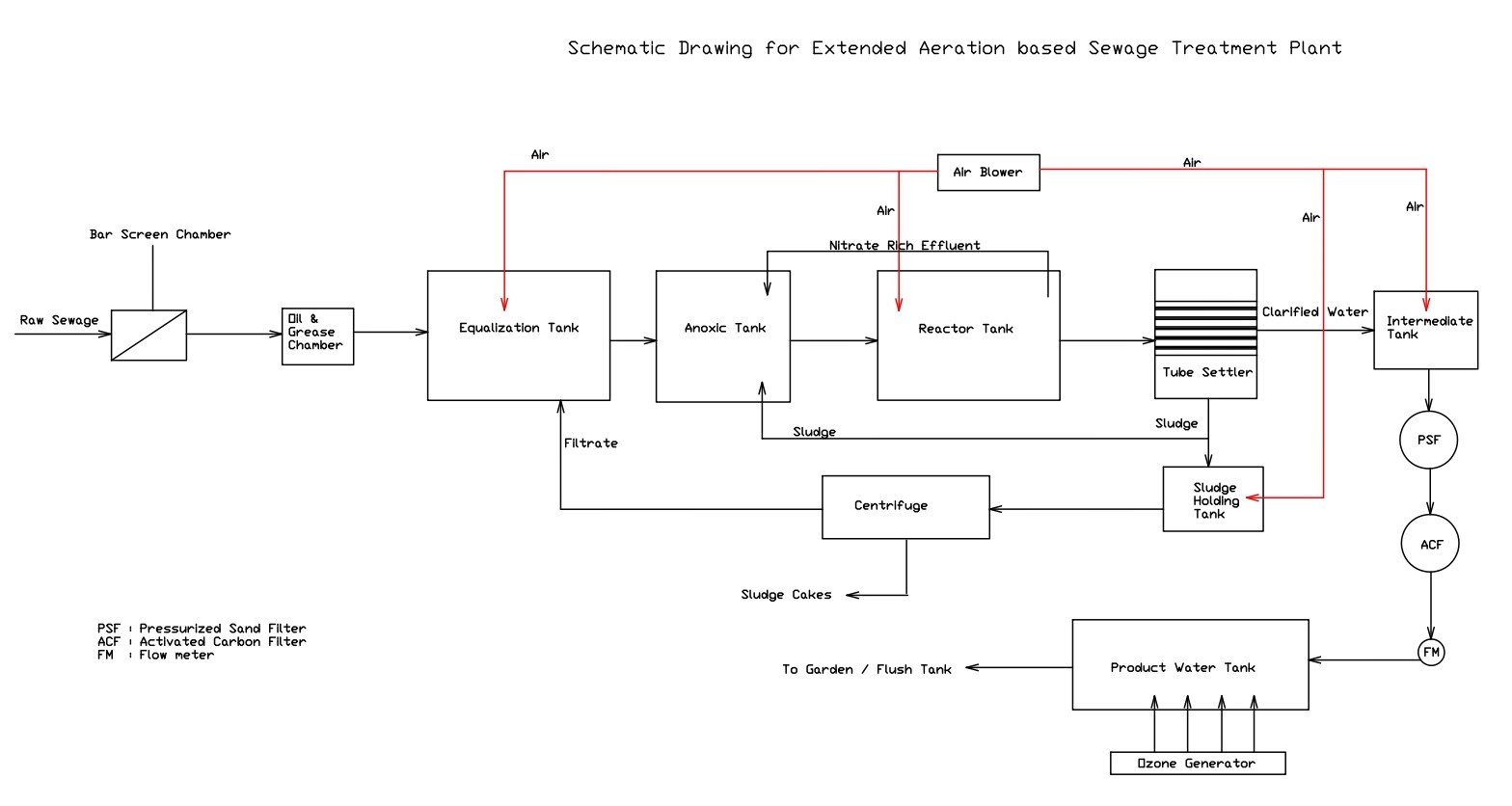
Advantages of Extended Aeration STP
Stable Operation
The extended aeration process provides a stable and consistent environment for microbial activity, reducing the impact of variations in influent characteristics.

Reduced Sludge Production
Extended aeration often results in lower sludge production compared to some other treatment processes. This can simplify sludge handling and disposal.

Simple Design
Extended aeration systems typically have a simple and straightforward design, making them suitable for smaller communities or decentralized treatment applications.

Energy Efficiency
While energy is required for aeration, the extended aeration process can be designed to optimize energy efficiency, especially in comparison to more intensive aeration processes.
Applications
Municipal Wastewater Treatment
Extended aeration STPs are commonly used in small to medium-sized communities, providing a cost-effective and efficient solution.
01.
Residential and Commercial Developments
Due to their simplicity and ease of operation, extended aeration systems are
suitable for residential and commercial developments with decentralized
wastewater treatment needs.
02.
Remote or Rural Areas:
In remote or rural areas where centralized sewer systems may not be feasible, extended aeration STPs can offer a practical and decentralized solution.
